Thursday 25 October 2018
Wednesday 24 October 2018
Monday 17 September 2018
Friday 14 September 2018
Sunday 9 September 2018
MCQ
QUESTION 1
In a postmenopausal woman with abnormal
vaginal bleeding who is not receiving hormone
replacement therapy, which of the following
endometrial thickness cutoff criteria is used to
optimize accuracy for detecting cancer?
A. ≥ 4 mm.
B. ≥ 5 mm.
C. ≥ 6 mm.
D. ≥ 7 mm.
E. ≥ 8 mm.
QUESTION 2 In a postmenopausal woman with abnormal vaginal bleeding who is undergoing hormone replacement therapy, which of the following endometrial thickness cutoff criteria is used to optimize accuracy for detecting cancer?
A. ≥ 4 mm.
B. ≥ 5 mm.
C. ≥ 6 mm.
D. ≥ 7 mm.
E. ≥ 8 mm.
A. ≥ 4 mm.
B. ≥ 5 mm.
C. ≥ 6 mm.
D. ≥ 7 mm.
E. ≥ 8 mm.
QUESTION 2 In a postmenopausal woman with abnormal vaginal bleeding who is undergoing hormone replacement therapy, which of the following endometrial thickness cutoff criteria is used to optimize accuracy for detecting cancer?
A. ≥ 4 mm.
B. ≥ 5 mm.
C. ≥ 6 mm.
D. ≥ 7 mm.
E. ≥ 8 mm.
Wednesday 6 June 2018
Monday 4 June 2018
PERFUSION IMAGING ---BASICS
-------Perfusion magnetic resonance
(MR) imaging techniques are
widely used in the clinical work-up
of brain tumors because of their ability
to help quantify tumor microvessel proliferation
and permeability and thus to
measure changes associated with neoangiogenesis,
which correlate with tumor
malignancy.
-----Dynamic susceptibility contrast (DSC) MR imaging has been extensively explored for glioma grading , for prognostic assessment , and for differentiating between recurrent tumor and posttreatment changes .
-----Dynamic contrast material–enhanced (DCE) MR imaging has been recently introduced in the preoperative assessment and follow-up of brain tumors.
------The DCE signal intensity– time curve reflects a combination of tissue perfusion, microvessel permeability, and extravascular-extracellular space , thus allowing for a multiparametric characterization of tumor microvasculature.
------The advantages of DCE over DSC are fewer susceptibility artifacts and the quantification of blood-brain barrier (BBB) integrity; indeed, the main interest for DCEderived metrics was initially focused on the volume transfer constant (Ktrans), a permeability marker correlating with BBB disruption and malignancy .
----The advantage of DSC over DCE is better temporal resolution, allowing better estimation of blood volume.
-----Dynamic susceptibility contrast (DSC) MR imaging has been extensively explored for glioma grading , for prognostic assessment , and for differentiating between recurrent tumor and posttreatment changes .
-----Dynamic contrast material–enhanced (DCE) MR imaging has been recently introduced in the preoperative assessment and follow-up of brain tumors.
------The DCE signal intensity– time curve reflects a combination of tissue perfusion, microvessel permeability, and extravascular-extracellular space , thus allowing for a multiparametric characterization of tumor microvasculature.
------The advantages of DCE over DSC are fewer susceptibility artifacts and the quantification of blood-brain barrier (BBB) integrity; indeed, the main interest for DCEderived metrics was initially focused on the volume transfer constant (Ktrans), a permeability marker correlating with BBB disruption and malignancy .
----The advantage of DSC over DCE is better temporal resolution, allowing better estimation of blood volume.
PRECISION MEDICINE/RADIOMICS/RADIOGENOMICS
----Precision medicine is medicine optimized to the genotypic and phenotypic characteristics of an individual and, when present, his or her disease. It has a host of targets, including genes and their transcripts, proteins, and metabolites.
----Studying precision medicine involves a systems biology approach that integrates mathematical modeling and biology genomics, transcriptomics, proteomics, and metabolomics.
----Moreover, precision medicine must consider not only the relatively static genetic codes of individuals, but also the dynamic and heterogeneous genetic codes of cancers. Thus, precision medicine relies not only on discovering identifiable targets for treatment and surveillance modification, but also on reliable, noninvasive methods of identifying changes in these targets over time.
---Imaging via radiomics and radiogenomics is poised for a central role.
-----Radiomics, which extracts large volumes of quantitative data from digital images and amalgamates these together with clinical and patient data into searchable shared databases, potentiates radiogenomics, which is the combination of genetic and radiomic data.
----- Radiogenomics may provide voxel-by-voxel genetic information for a complete, heterogeneous tumor or, in the setting of metastatic disease, set of tumors and thereby guide tailored therapy.
-----Radiogenomics may also quantify lesion characteristics, to better differentiate between benign and malignant entities, and patient characteristics, to better stratify patients according to risk for disease, thereby allowing for more precise imaging and screening.
REF --RADIOLOGY
Saturday 2 June 2018
TELE -BILI-PAQUE
Q1..All are true regarding Telepaque and Bilipaque except
a.bilopaque is better choice than Telepaque in patients
with enterrupted enterohepatic circulation
b.Telepaque is more lipid –soluble than Bilopaque
c.peak contrast concentration occurs after approx.10 hrs
after Bilopaque ingestion
d.the usual dose of Telepaque is 6 tabs after evening
meal
e.patients must take fat after ingetion of Telepaque
ANS.---e
Patients
must not take anything except water after ingestion of Telepaque
Q2..All are causes of non visualisation of the gall bladder during oral
cholecystography except
a.esophageal /gastric/small intestinal obstruction
b.Crohn disease
c.disruption of renal circulation
d.hepatic dysfunction
e.acute/chronic cholecystitis
ANS.---c
Disruption
of entero-hepatic circulation is one of the cause of non –visualisation of gall
bladder
Thursday 3 May 2018
GATEWAY TO LIVER ( PORTA)
Q.All are true regarding anatomy of hepatobiliary system except
a.The porta is fat filled space
b.Bile duct act as landmark for the anterolateral margin
of
pancreatic head
c.The intraduodenal segment of bile duct is approx 1 to
2cm
d.Spiral valves of Heister is located in the neck of gall
bladder
e.Phgrygian cap is
due to folding of gall bladder fundus on itself
ANS.---b
Bile
duct act as landmark for the postero-lateral margin of
pancreatic head.The
gastroduodenal artery acts as landmark of
anterolateral margin of the
pancreatic head
Wednesday 11 April 2018
First step in fetal echo----visceral situs
Visceral situs ( determination of laterality of fetal organs)
----first step in fetal echo ---why? allow for accurate determination of atrial and
ventricular situs
----Three types of visceral situs
1.situs solitus---normal arrangement of vessels and organs within the body
2.situs inversus---mirror image arrangement of organs and vessels to situs solitus(.01% of population ),slight increase in complex CHD
3.situs ambiguus(heterotaxy) ,incidence --1per 10,000 infants,commonly associated with complex CHD
Two types of heterotaxy
a.Right isomerism( asplenia)---both sides of body show the right morphology
b.Left isomerism( polysplenia)--both sides of body show the left morphology
SITUS SOLITUS
RIGHT SIDE LEFT SIDE
Morphologic right atrium Morphologic left atrium
major hepatic veins Stomach
IVC Descending aorta
short eparterial bronchus Long hyparterial bronchus
TECHNIQUE
1.Locate the fetal head within the uterus and determine the presenting part ( cephalic,breech etc)
2.Determine the fetal lie within the uterus by obtaining the saggital view of the fetal spine ( longitudinal ---when fetal spine is parallel to maternal spine /transverse---when fetal spine is perpendicular to the maternal spine / oblique lie ---when the fetal spine is oblique to the maternal spine )
3.Determine the location of fetal left side with regard to maternal abdomen ( anterior/posterior /right lateral/left lateral )
4.Obtain the transverse view of the fetal abdomen by rotating the transducer 90 degrees from the saggittal view of the lower thoracic spine .
The fetal stomach is imaged in the left side of the abdomen,the descending aorta is posterior to the left and IVC is anterior to the right .
Now slide the transducer toward the fetal chest to obtain the four- chamber view of the heart .
The apex of the heart points toward the left side of the fetal chest .
Determining that the stomach ,descending aorta and the cardiac apex are located on the fetal left side and the IVC is located on the right side establishes normal visceral situs
There are other methods to determine the visceral situs like Cordes et al and right and left hand rule of Bronshtein
----first step in fetal echo ---why? allow for accurate determination of atrial and
ventricular situs
----Three types of visceral situs
1.situs solitus---normal arrangement of vessels and organs within the body
2.situs inversus---mirror image arrangement of organs and vessels to situs solitus(.01% of population ),slight increase in complex CHD
3.situs ambiguus(heterotaxy) ,incidence --1per 10,000 infants,commonly associated with complex CHD
Two types of heterotaxy
a.Right isomerism( asplenia)---both sides of body show the right morphology
b.Left isomerism( polysplenia)--both sides of body show the left morphology
SITUS SOLITUS
RIGHT SIDE LEFT SIDE
Morphologic right atrium Morphologic left atrium
major hepatic veins Stomach
IVC Descending aorta
short eparterial bronchus Long hyparterial bronchus
TECHNIQUE
1.Locate the fetal head within the uterus and determine the presenting part ( cephalic,breech etc)
2.Determine the fetal lie within the uterus by obtaining the saggital view of the fetal spine ( longitudinal ---when fetal spine is parallel to maternal spine /transverse---when fetal spine is perpendicular to the maternal spine / oblique lie ---when the fetal spine is oblique to the maternal spine )
3.Determine the location of fetal left side with regard to maternal abdomen ( anterior/posterior /right lateral/left lateral )
4.Obtain the transverse view of the fetal abdomen by rotating the transducer 90 degrees from the saggittal view of the lower thoracic spine .
The fetal stomach is imaged in the left side of the abdomen,the descending aorta is posterior to the left and IVC is anterior to the right .
Now slide the transducer toward the fetal chest to obtain the four- chamber view of the heart .
The apex of the heart points toward the left side of the fetal chest .
Determining that the stomach ,descending aorta and the cardiac apex are located on the fetal left side and the IVC is located on the right side establishes normal visceral situs
There are other methods to determine the visceral situs like Cordes et al and right and left hand rule of Bronshtein
Monday 2 April 2018
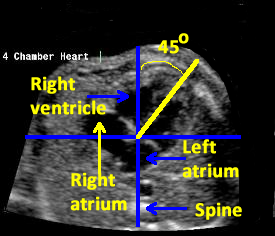
FETAL ECH---FOUR CHAMBER VIEW
--Fetal echo detects majority of structural cardiac abnormalities.
---most neonates born with CHD have no preidentified risk factors.
---prenatal detection rates of isolated CHD have remained below 50% in the general population
---Four chamber view and the outflow tracts are used for prenatal detection of CHD
---Outflow tracts view of fetal heart show better detection of CHD when compared to the four chamber view
---Nuchal translucency ( 10 -14 weeks) greater than or equal to 3,55 mm is an indication for fetal echo
Criteria of normal four chamber view of heart
1.normal fetal situs
2.normal size in relation to chest
3.the two atria a---equal in size and the flap of the foramen ovale is seen in the left atrium
4.the venticles are equal in size and contactility ,moderator band in the apex of right ventricle
5.atrial and ventricular septae are normal appearing
6.the AV valves are normal appearing .the tricuspid valve appears to insert more apically on the ventricular septum
CARDIAC ABNORMALITIES associated with abnormal four-chamber view of the heart
1.mitral/aortic atresia
2.tricuspid /pulmonary atresia
3.Ebstein anomaly /tricuspid valve dysplasia
4.AV septal defect
5.large VSD
6.single ventricle (double inlet)
7/severe/aortic /pulmonary stenosis
8.severe coarctation of aorta
9.TAPVC
10.cardiomyopathies /tumour
CARDIAC ABNORMALITIES associated with NORMAL four-chamber view of the heart
1.TOF
2.TGA
3.double outlet right ventricle
4.small VSD
5.common arterial trunk
6.aortic arch abnormalities
Saturday 31 March 2018
RISK FACTORS OF CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE
RISK FACTORS OF CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE
FETAL
---Chromosomal abnormalities
---extracardiac anatomic abnormalities ( nonimmune hydrops ,single umblical artery ,renal agenisis omphalocoele etc)
---fetal cardiac arrhythmia
---suspected cardiac anomaly on routine usg
---thickened nuchal translucency(>/-3.5mm)
---monochorionic plancentation
MATERNAL
----Family history of CHD
----maternal metabolic disorder ( diabetes ,PKU)
---maternal teratogen exposure (lthium,hydantoin,valproic acid ,ethanol,isotretinoin,ACE inhibitors ,SSRIs)
---pregnancy of assisted reproduction
---maternal obesity
FETAL
---Chromosomal abnormalities
---extracardiac anatomic abnormalities ( nonimmune hydrops ,single umblical artery ,renal agenisis omphalocoele etc)
---fetal cardiac arrhythmia
---suspected cardiac anomaly on routine usg
---thickened nuchal translucency(>/-3.5mm)
---monochorionic plancentation
MATERNAL
----Family history of CHD
----maternal metabolic disorder ( diabetes ,PKU)
---maternal teratogen exposure (lthium,hydantoin,valproic acid ,ethanol,isotretinoin,ACE inhibitors ,SSRIs)
---pregnancy of assisted reproduction
---maternal obesity
Sunday 11 February 2018
CT NO OF LIVER
6 Q.Which cause significant increase of CT
no of
liver
a.fatty liver
b.fibrosisc.increased cu content
d.gycogen
e.none
ANS---e
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)








