Multimodal MR Imaging of Brain Iron in Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder: A Noninvasive Biomarker That Responds to Psychostimulant Treatment?
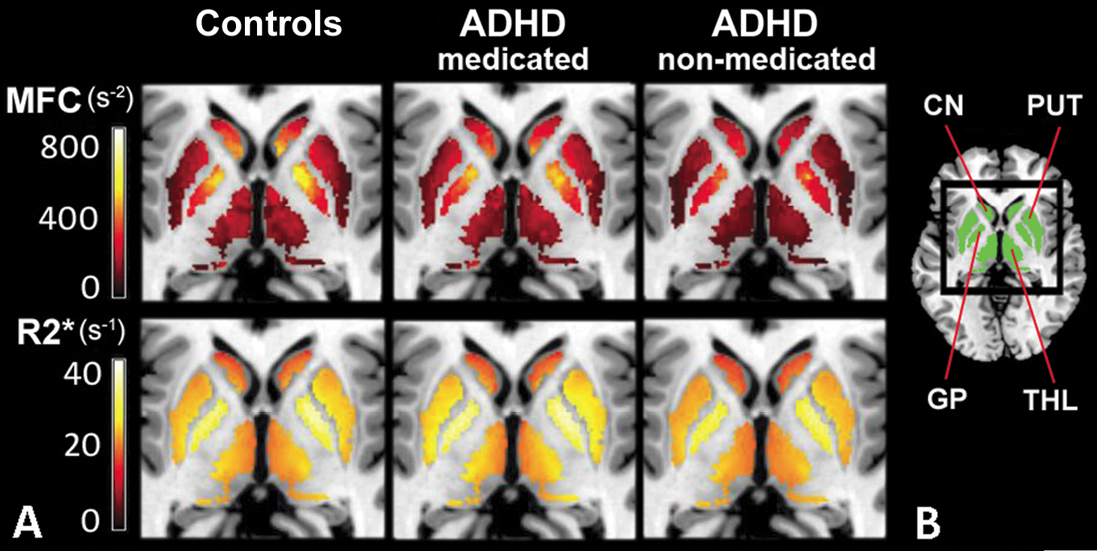
Lower magnetic field correlation (MFC) indexes of striatal and thalamic brain iron in medication-naïve attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) patients and lack of differences in psychostimulant-medicated patients suggest that MFC indexes of brain iron may represent a noninvasive diagnostic biomarker that responds to psychostimulant treatment
Vitria Adisetiyo, Ph.D., of the Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston, and colleagues prospectively examined 22 patients with ADHD (12 medication-naïve patients and 10 with a history of psychostimulant treatment) and 27 control subjects (age range, 8 to 18 years). Brain iron was indexed noninvasively using MR imaging relaxation rates (R2, R2*, R2') and MFC in the globus pallidus, putamen, caudate nucleus and thalamus. Serum iron measures were also collected. Subgroup differences were analyzed with data-appropriate omnibus tests followed by post-hoc pairwise comparisons; false discovery rate correction was conducted to control for multiple comparisons.
Medication-naïve ADHD patients had significantly lower striatal and thalamic MFC indexes of brain iron than control subjects (putamen, P = .012; caudate nucleus, P = .008; thalamus, P = .012) and psychostimulant-medicated ADHD patients (putamen, P = .006; caudate nucleus, P = .010; thalamus, P = .021). Conversely, the MFC indexes in medicated patients were comparable to those in control subjects. No significant differences were detected with R2, R2*, R2' or serum measures.
“Our results implicate reduced striatal and thalamic brain iron levels in ADHD pathophysiology before medication and suggest that reduced brain iron levels may normalize with psychostimulant treatment,” the authors write.