Visceral situs ( determination of laterality of fetal organs)
----first step in fetal echo ---why? allow for accurate determination of atrial and
ventricular situs
----Three types of visceral situs
1.situs solitus---normal arrangement of vessels and organs within the body
2.situs inversus---mirror image arrangement of organs and vessels to situs solitus(.01% of population ),slight increase in complex CHD
3.situs ambiguus(heterotaxy) ,incidence --1per 10,000 infants,commonly associated with complex CHD
Two types of heterotaxy
a.Right isomerism( asplenia)---both sides of body show the right morphology
b.Left isomerism( polysplenia)--both sides of body show the left morphology
SITUS SOLITUS
RIGHT SIDE LEFT SIDE
Morphologic right atrium Morphologic left atrium
major hepatic veins Stomach
IVC Descending aorta
short eparterial bronchus Long hyparterial bronchus
TECHNIQUE
1.Locate the fetal head within the uterus and determine the presenting part ( cephalic,breech etc)
2.Determine the fetal lie within the uterus by obtaining the saggital view of the fetal spine ( longitudinal ---when fetal spine is parallel to maternal spine /transverse---when fetal spine is perpendicular to the maternal spine / oblique lie ---when the fetal spine is oblique to the maternal spine )
3.Determine the location of fetal left side with regard to maternal abdomen ( anterior/posterior /right lateral/left lateral )
4.Obtain the transverse view of the fetal abdomen by rotating the transducer 90 degrees from the saggittal view of the lower thoracic spine .
The fetal stomach is imaged in the left side of the abdomen,the descending aorta is posterior to the left and IVC is anterior to the right .
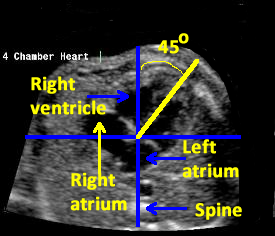
Now slide the transducer toward the fetal chest to obtain the four- chamber view of the heart .
The apex of the heart points toward the left side of the fetal chest .
Determining that the stomach ,descending aorta and the cardiac apex are located on the fetal left side and the IVC is located on the right side establishes normal visceral situs
There are other methods to determine the visceral situs like Cordes et al and right and left hand rule of Bronshtein
----first step in fetal echo ---why? allow for accurate determination of atrial and
ventricular situs
----Three types of visceral situs
1.situs solitus---normal arrangement of vessels and organs within the body
2.situs inversus---mirror image arrangement of organs and vessels to situs solitus(.01% of population ),slight increase in complex CHD
3.situs ambiguus(heterotaxy) ,incidence --1per 10,000 infants,commonly associated with complex CHD
Two types of heterotaxy
a.Right isomerism( asplenia)---both sides of body show the right morphology
b.Left isomerism( polysplenia)--both sides of body show the left morphology
SITUS SOLITUS
RIGHT SIDE LEFT SIDE
Morphologic right atrium Morphologic left atrium
major hepatic veins Stomach
IVC Descending aorta
short eparterial bronchus Long hyparterial bronchus
TECHNIQUE
1.Locate the fetal head within the uterus and determine the presenting part ( cephalic,breech etc)
2.Determine the fetal lie within the uterus by obtaining the saggital view of the fetal spine ( longitudinal ---when fetal spine is parallel to maternal spine /transverse---when fetal spine is perpendicular to the maternal spine / oblique lie ---when the fetal spine is oblique to the maternal spine )
3.Determine the location of fetal left side with regard to maternal abdomen ( anterior/posterior /right lateral/left lateral )
4.Obtain the transverse view of the fetal abdomen by rotating the transducer 90 degrees from the saggittal view of the lower thoracic spine .
The fetal stomach is imaged in the left side of the abdomen,the descending aorta is posterior to the left and IVC is anterior to the right .
Now slide the transducer toward the fetal chest to obtain the four- chamber view of the heart .
The apex of the heart points toward the left side of the fetal chest .
Determining that the stomach ,descending aorta and the cardiac apex are located on the fetal left side and the IVC is located on the right side establishes normal visceral situs
There are other methods to determine the visceral situs like Cordes et al and right and left hand rule of Bronshtein